|
Lecture Notes Supplement on CES Economics of the Environment and Natural Resources/Economics of Sustainability K Foster, CCNY, Spring 2011 |
|
|
Note on CES utility functions
Some papers use a Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) utility function in the economic theory. These are common but used not so much for their realism but to simplify some of the formulas.
A CES utility has a general form of
,
which looks a bit awful but is "simple" insofar as it makes later formulas so.
Since people make decisions on the margin, we look at marginal utility, which is the derivative,
.
At optimum, C is chosen to make the price, P, equal to Marginal Utility (MU), so
,
which is the demand curve. Plot it and note it has a general shape as:
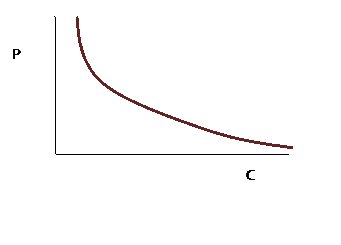
which looks "like a demand curve should."
The elasticity of demand at any point is , and we can find by taking the derivative of the demand curve, , . Substitute into the elasticity equation for P and the derivative, to get
.
A constant elasticity, as promised.